Know-How Toner technologies: Different types of toner
There are a number of different types of toner, which mainly differ in their way of production. All of them is in common that they have to be fixed on paper at high temperatures, occasionally up to 200 degrees. Not all papers can stand these temperatures. So you must not use any coated papers, because they may become wavy in this process.
A basic distinction: One- and two-component toner:
- For One-component toner you need only one cartridge for each color. Each contains a mixture of toner and developer. Their advantage is the easy maintenance, the disadvantage are higher costs. Since the developer also remains on the printed paper, it is supposed not distort the colors. You will find one-component in most common mono and color lasers.
- With Two-component toner developer and toner are in separate containers. As developer often very fine iron particles are used, which are not applied to the paper, but go to the waste container. The advantage of two-component toner is the simpler construction of the toner cartridge, resulting in a lower price. Disadvantages: Toner and developer have to be refilled separately, and the construction of the printing devices is more complicated. Two-component toner is used mainly in large copiers and digital printing machines.
Mechanically produced toner
Classic toner powder, also known as conventional or ground toner, is produced in a mechanical way. It´s components are melted by heating and high mechanical forces in an Extruder ![]() .
.
The resulting homogeneous, viscous liquid is cooled, rolled onto a large area to a thin layer, and dried. Thereafter, the solidified mass is pre-crushed and then ground coarsely to the target size of the particles.
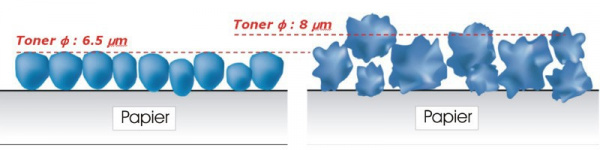
Depending on the material used the milling process requires a lot of time and energy, resulting in high costs. Therefore he limit of economic production is at a grain size from 6.5 to 7 micrometers in diameter*1.
The toner particles are irregular in shape and size, like crushed rock. Consequently small particles have problems to get in contact with the paper due to the larger particles around them. So the ratio of toner used to toner actally used for printing isn´t optimal. Print quality is affected as well: The larger the particles, the lower the print quality, and vice versa.
Another disadvantage of conventional toners is the thickness of five to seven microns of the toner layer on the paper - with chemical toners, it is only two to three microns.
However, there are advantages as well. Conventional toner offers a larger color space compared to chemically produced toner - so brighter and more brilliant colors are available.
Chemically produced toner
Chemically produced toners have been around since the 1990s. They are marketed under various names - by Xerox as EA (Emulsion Aggregation) toner or Konica-Minolta as Simitri HD toner.
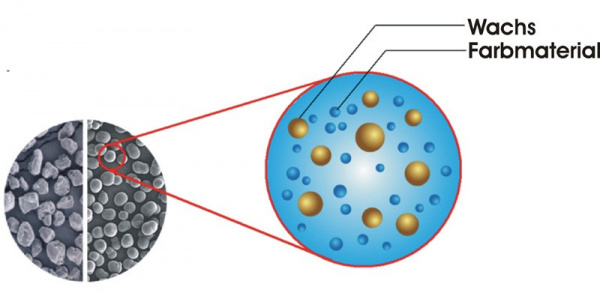
The production of chemical toner aims to produce as small, round and uniformly shaped particles as possible. For this, the toner particles grow in an emulsion of water, wax, and latex polymer, that contains all the ingredients of the toner. By a layer by layer deposition, tiny beads of toner particles are forming, which grow as long until they are removed from the liquid.
Advantageous in the chemical manufacturing process is that it is possible to produce dry toner particles in any shape, size and with differnt characteristics. The entire process can be precisely controlled via temperature, time, and pH. Subsequently chemical toner is shaped much more evenly than conventional toner.
Only about half as large and regularly shaped the particles of the chemical toner provide a more economical color application by 30-40 per cent in contrast to conventional toners. Printing results show more subtleties, and gradations of halftone patterns and colors and intricate patterns are printed sharper and more accurately.
In addition, all colored toners have an identical charge behavior and are only negligibly dependent on environmental conditions. This way all prints basically come out always the same way, and the colors are more stable.
Moreover, as the melting temperature of chemical toner is lower than of conventional toner, it can be fixed at lower temperatures. In this way energy is saved and a larger selection of papers for printing is available.
Another advantage of many chemically produced toner is the oil-free fixing process. While oil is necessary for the fixation of conventional toner on paper, wax is often added to chemical toners as a fixative. In the printing process, wax is released and fixes the toner only in places, where color (toner) is applied. This improves print quality because the colors look more vivid and natural, do not fade quickly, and are less shiny. Prints created without the oil film can be written on with ink, or adhesive labels can be attached to it.



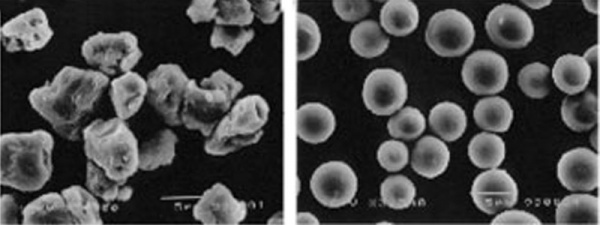
 Under the microscope: Particles of conventional (left) and chemically prepared toner (right) differ significantly - Source: Xerox.
Under the microscope: Particles of conventional (left) and chemically prepared toner (right) differ significantly - Source: Xerox.